I know I'm not alone in feeling that at this moment in time and history, I need all my self-care skills and then some. The Alexander Technique is at the top of my list.
Read moreConfession of a Prejudiced Woman
Full disclosure: I marched against the Vietnam War years ago and much later against the war in Iraq. I eat kale and arugula. I volunteered and voted for Hillary Clinton, and have been in mourning ever since election day. Having said that, I will add that this is not a political blog!
Read moreNothing to Know: Writing and Living with The Alexander Technique
Writing with a soft gaze and a loose grip around the pen might mean that you make more of a mess. And the thoughts that make their way to paper might be more of a wandering than an answer. A spiral of questions. Some what-ifs, whys and maybes.
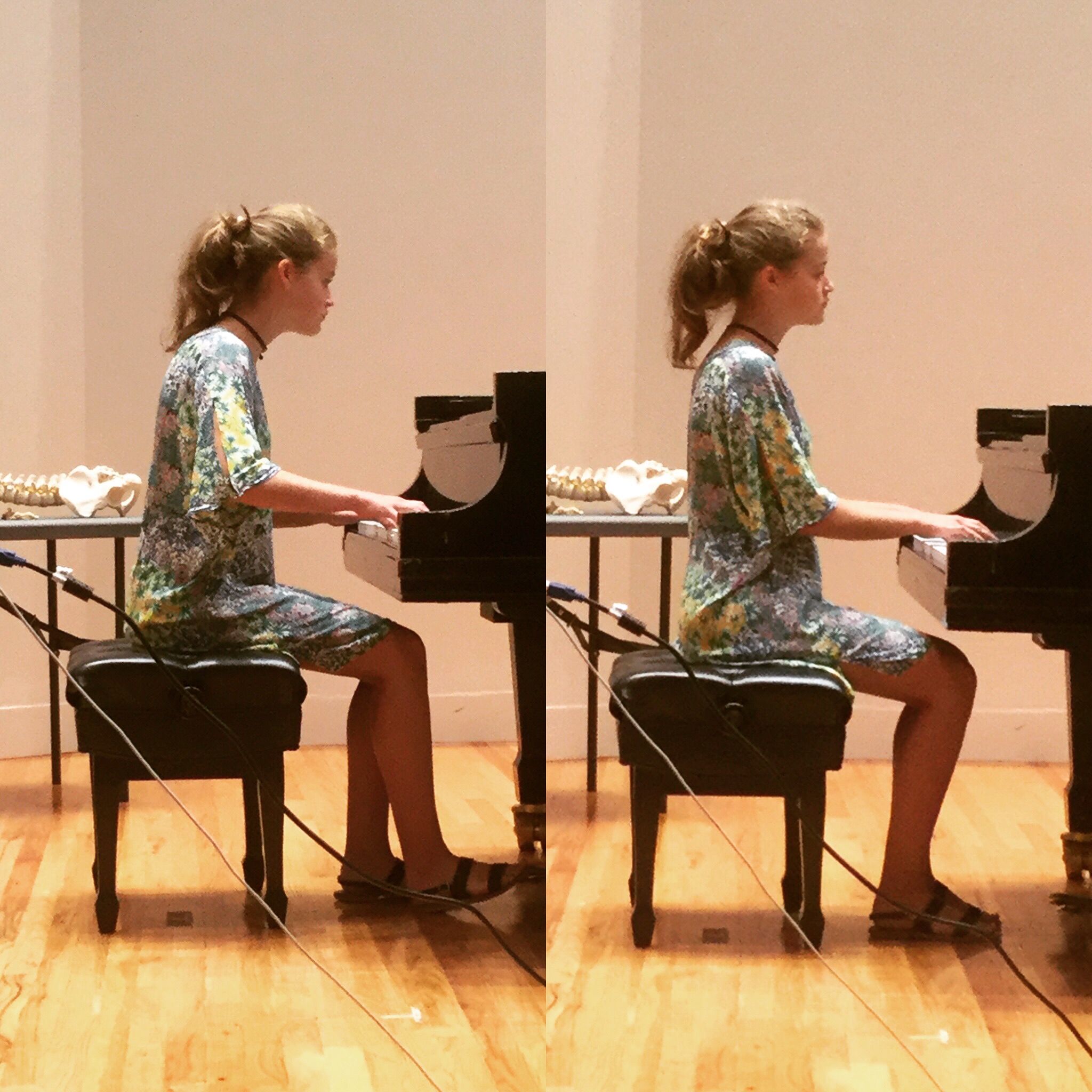
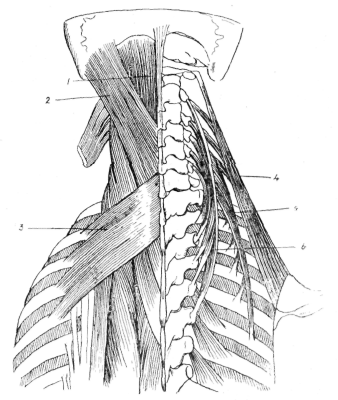
Read moreBody Mapping and the Alexander Technique
I began my relationship with Body Mapping in my early days as a college music student, little did I know how much of my future would be determined by simply registering for this course that came so highly recommended.
Read moreAlice Olsher and The Carrington Games (Upcoming Workshop)
Alice Olsher taught the Post Graduate Program "The Carrington Games: From the Basics of Self-Care" to Training Teachers on January 14 & 15.
Read moreAlexander Technique at Political Demonstrations
I’m not advising you on who or what to protest, but I marched on Sunday at a big anti-Trump rally in Midtown Manhattan. As I was remembering my Alexander principles, I came up with a few guidelines for participating in the demonstration or march of your choice.
Read moreElection Cycle Fatigue: What you can do to take care of yourself and those around you
by Brooke Lieb The first time I voted in a Presidential election was 1984. My memory is far from perfect, but I cannot recall a presidential race that began as early as the 2016 race, with one party's campaigning for the nomination starting in March, 2015; nor can I remember the type of rhetoric I am hearing as overt and extreme in US politics as it is during this election.
Frankly, it frightens me. And I am not alone. There are a plethora of articles about the heightened anxiety levels precipitated by this current election cycle. A search for "election anxiety" yields online articles from The Atlantic, US News, Newsweek, Time Magazine and The Washington Post, among other news outlets.
As an Alexander teacher, I spend my days teaching my students how to self-regulate so they can manage moments of spiking anxiety. To be an effective teacher, I use the very tools I am teaching, at work and in my life.
No matter which side of this debate you are on, it is likely that you feel strongly, believe in your own point of view and fear the outcome. It is also likely that your feelings are being heightened by the coverage you are exposed to.
What can you do to take care of yourself? Here are some resources, including simple tools I teach my students.
1. Remind yourself that you don't have to hold your breath.
When we experience fear or other strong emotions, we sometimes freeze. It may be a tight jaw, it may be subtle or not so subtle clenching in shoulder, chest or abdomen. Frequently, tension reduces the mobility of our torso, and breath requires movement in the ribs.
2. Stand with your back touching a wall or door.
Use the contact with your back against the surface to bring you into the present environment. See and name what is around you, in as much detail as you can. (Example from my studio: Area rug with floral patterns, in beige, burgundy, sage green; massage table with a green cotton sheet that has stripes; dark brown wood computer desk with a cordless phone/answering machine and an iMac; fireplace mantle surrounded by teal tiles).
3. Research what actions you can take to assure your vote counts and that your elected officials represent your values.
Search your state and federal nominees to find out where they stand on the issues (search "[your state] 2016 candidate platforms". In addition to finding out where they stand, you can find out how to support the campaign of those who represent your views.
4. Learn how to bring awareness to, change the subject, and minimize participation in conversations that upset you.
It is possible to effectively bring awareness and shift the conversation without shaming anyone. This article from the New York Times is entitled "Lessons in the Delicate Art of Confronting Offensive Speech"
5. If someone has decided who they are voting for, there is no need for discussion. If speaking to an undecided voter, learn how to listen to what matters to that person.
Here is an article "5 Ways To Have Great Conversations"
6. Limit your exposure to media
Once you have done your research and know which candidates represent your values, and how you can take action to improve their chances in the election, take a media vacation. This has not been easy for me, but I have designated media black out days, when I do not read or watch anything about the election.
7. Have an Alexander Lesson
Alexander Technique teaches mindfulness in daily living. Akin to meditation, Alexander Technique teaches conscious inhibition, or how to calm your "flight or fight" response.
This article in Wikipedia explains the neural mechanisms of mindfulness techniques.
This blog was originally posted at brookelieb.com
[author] [author_image timthumb='on']http://www.acatnyc.org/main/wp-content/uploads/2014/01/Brooke1web.jpg[/author_image] [author_info]N. BROOKE LIEB, Director of Teacher Certification since 2008, received her certification from ACAT in 1989, joined the faculty in 1992. Brooke has presented to 100s of people at numerous conferences, has taught at C. W. Post College, St. Rose College, Kutztown University, Pace University, The Actors Institute, The National Theatre Conservatory at the Denver Center for the Performing Arts, Dennison University, and Wagner College; and has made presentations for the Hospital for Special Surgery, the Scoliosis Foundation, and the Arthritis Foundation; Mercy College and Touro College, Departments of Physical Therapy; and Northern Westchester Hospital. Brooke maintains a teaching practice in NYC, specializing in working with people dealing with pain, back injuries and scoliosis; and performing artists. www.brookelieb.com[/author_info] [/author]
Alexander Student, Alexander Teacher, Alexander Teacher Trainer - What's the difference, and why does it matter?
 by Brooke Lieb
I have been taking lessons as a student of the Alexander Technique for over 33 years. I still take lessons to this day.
by Brooke Lieb
I have been taking lessons as a student of the Alexander Technique for over 33 years. I still take lessons to this day.
I began teaching 27 years ago, and have been training teachers for the last 25 years.
My greatest passion is training teachers, though I will take lessons for the rest of my life, and I get deep satisfaction teaching my private students.
I thought it would be useful to me, my students and the teachers-in-training that I work with, to consider what is different about each of these roles: student, teacher, teacher-trainer.
STUDENT
When I take a lesson, my attention is on myself. I gratefully accept the objectivity of my teacher as she uses her hands and words to engage me in learning. My learning takes place on many levels.
My teacher's hands are giving me information and experiences that assist my ability to observe and know how much excess tension I may be generating in my being. I am using my lessons to enhance the benefit I gain in my daily life when I bring my Alexander Technique tools to bear.
Sometimes the excess tension arises in response to a muscular demand, in activity, involving motion. We might explore how I carry out the activity of getting in and out of a chair, use my handheld device, or move into and out of downward dog during yoga practice.
I might observe excess tension in the context of my inner dialogue. Thinking about my workload, administrative tasks I have yet to complete, my response to someone's actions.
Any and every activity, mental or physical, can be material for the lesson.
Whatever I am exploring, I am interested in my own skills. I allow my teacher to be my guide and to educate me about myself and how I can best use my Alexander skills to access the efficiency and intelligence of being a human.
I have no focus whatsoever on assessing my teacher's use or process, I trust she is my guide. I am grateful and appreciative for the support and benefit I receive from the lesson and her teaching.
TEACHER
In contrast, when I am the teacher, my level of awareness is expanded to observe how my student is progressing, as I observe how I am teaching.
What skills might she benefit from learning or deepening during this lesson?
How can I use the hands-on component of the work to help guide her into a more integrated and poised state?
Private students (including me) take lessons for self-benefit, so they are focused on applying the Alexander principles to aid them in their lives. They are not planning to teach the work to anyone else. Their attention is NOT on the teacher.
As the teacher, I manage my end-gaining, and apply the principles to myself in the activity of teaching (hands-on work; choosing where to put my hands; what concept I may emphasize in the moment or in the lesson; speaking; and utilizing instructional aids, such as pictures of anatomy and videos). I use Alexander's means-whereby to teach, i.e., I am using the very same skills I am teaching in order to teach effectively.
As a teacher, my attention is on my student, her goals for learning and applying Alexander Technique to solve her own problem. That dual attention leaves me less time to wander around in my own mental chatter, so teaching becomes an activity that supports me in inhibiting my own habits on multiple levels.
I also benefit directly in my own self from working with Alexander principles, even if I am the "teacher" in this situation. When I give a lesson, I get a lesson.
My work is as healthy and beneficial to me as it is to my student.
TEACHER TRAINER
In this role, I am adding a level of assessment for how self-sufficient the teacher-in-training (trainee) is when working on herself, and as she reaches a high level of competence, I assist her in applying her means-whereby to teaching.
On our training course at The American Center for the Alexander Technique (ACAT), our trainees regularly put hands on faculty members as a tool for training. This approach is educational on multiple levels:
1) Faculty members all have a high level of competence at applying means-whereby to activity, so in the same way we use our hands on our trainees to convey inhibition and direction, when our trainees put their hands on us, we are still transmitting that information through our whole bodies. As the trainee progresses through the three-year training, she recognizes what she is witnessing under her hands, and with her eyes and ears. She has worked with classmates, and practice students with less skill, and can compare and contrast what she has observed under her hands. This gives her a sense of the kind of changes and progress she may observe in her students, so she knows that learning and change really are happening over time.
2) When a trainee works on a faculty member, we give specific verbal and hands-on cues so the trainee can observe how a change in her system facilitates a change in the teacher she has hands on. Sometimes the change is towards enhanced poise and efficiency, sometimes the change is towards increased strain, effort or tension in muscle tone. Either way, observing the change allows the trainee to consider her own internal state, use her developed skills at self-work, and observe the change in the teacher-trainer she is working with. This is the means-whereby of teaching in action.
3) As the trainee works with faculty, she realizes we all have habits of use that interfere with our full potential for poise and efficient coordination. The trainee can provide valuable instruction to the trainer, and can also understand that a teacher's use need NOT be perfect for a teacher to be highly skilled and effective in our teaching.
I theorize that when a teacher has hands on and is working with her skills to inhibit and direct in herself in order to communicate that to her student, that process is discernable to the student. It may be so subtle the student is not yet aware of how the teacher's use is facilitating ease and poise, but the intention comes through. So even if the teacher is sometimes tightening her neck in moments, she is ALSO freeing her neck and using inhibition and awareness. That intention is picked up by the student, who is also providing inhibition and direction in the lesson. Student and teacher assist each other in this process. Both startle and pull down in moments, but both ALSO apply inhibition and direction to antidote startle and pull down.
In Closing
In some ways, the same means-whereby is in play in all three distinct roles, but there are clear differences in the short-term outcomes for learning and how this is accomplished in these three roles.
This post was originally published on brookelieb.com
[author] [author_image timthumb='on']http://www.acatnyc.org/main/wp-content/uploads/2014/01/Brooke1web.jpg[/author_image] [author_info]N. BROOKE LIEB, Director of Teacher Certification since 2008, received her certification from ACAT in 1989, joined the faculty in 1992. Brooke has presented to 100s of people at numerous conferences, has taught at C. W. Post College, St. Rose College, Kutztown University, Pace University, The Actors Institute, The National Theatre Conservatory at the Denver Center for the Performing Arts, Dennison University, and Wagner College; and has made presentations for the Hospital for Special Surgery, the Scoliosis Foundation, and the Arthritis Foundation; Mercy College and Touro College, Departments of Physical Therapy; and Northern Westchester Hospital. Brooke maintains a teaching practice in NYC, specializing in working with people dealing with pain, back injuries and scoliosis; and performing artists. www.brookelieb.com[/author_info] [/author]
New Group Class: Experiential Anatomy and Alexander Technique
 Experiential Anatomy and Alexander Techniquewith Witold Fitz-Simon
Experiential Anatomy and Alexander Techniquewith Witold Fitz-Simon
Tuesday Evenings (see dates below)
Learn to see, understand and talk about anatomy with an Alexander Technique twist. In this 10-week class, we will learn about bone, its physiology, function and use as a support structure and foundation for movement, with a special focus on the head and spine. This class is part of the American Center for the Alexander Technique's teacher-training program, the longest-running program in the US, but is open to anyone interested in the body and the way we use ourselves. Excellent for teachers of dance, yoga or other movement modalities, and for anyone interested in how their bodies work.
Class Day/Time: Tuesdays, 7:55 pm to 9:15 pm Class dates: September 13, 20, 27 October 25 November 1, 8, 15, 22 and 29 December 6 Class Fees: $400 for 10 classes; $45 per drop in class All fees are payable by cash or check to “ACAT” To register for the whole series: send $400 payment in full* to ACAT, 39 West 14th Street, Room #507, between 5th and 6th Avenue or click below to pay via PayPal (processing fees apply) Buzz #507 to enter the building *There are no refunds for missed classes
Riding the Wonder Wheel at Coney Island: How to manage a fear of heights with the Alexander Technique*
 by Brooke Lieb
*I recommend NOT riding the ferris wheel in the first place, but if you do find yourself having to manage your fear of heights, at least you might be able to ease some of the discomfort.
by Brooke Lieb
*I recommend NOT riding the ferris wheel in the first place, but if you do find yourself having to manage your fear of heights, at least you might be able to ease some of the discomfort.
In early August 2016, I joined a friend of mine on her birthday adventure to Coney Island. There were three other friends joining us, and the five us rode the F train to the last stop. Our first stop was the 150 foot high Wonder Wheel. The birthday person vetoed the moving cars, the ones that swing along the spokes, towards and away from the center of the wheel, in favor of a stationary car, which had instructions “Do Not Swing This Car” repeatedly posted outside the ride and inside our car.
We bought a discount ticket – Five rides for $30.
There was no line, and there weren’t many people on the ride. That would mean less stops as riders got off and on, so this would be over soon enough.
I got in the back with one other woman, and our Birthday person and her two remaining friends got in front.
My seat companion began to tense up the moment we began our ascent. She expressed her discomfort at heights, and I could see she was starting to panic, just a bit.
“I don’t like heights, either” I said. “This is what we’re going to do. Let’s both move into the middle of the car. Look down at the floor, at our feet. I’m going to hold your hand, and we’re going to breath together. I bet your heart is pounding like a scared rabbit in your chest, I know mine is!”
“Yes, it is…” she said.
“Now, as you’re breathing, if you can think about releasing any tension at the nape of your next, that can help to.”
We managed to look out at the view, part of the time. We kept periodically stopping, rocking in the air and hearing the creaking sound of metal as riders were let off and on the ride. There was no way I could pretend this wasn’t happening.
I held my seat mate’s hand, and tried to see what else was happening, as I took comfort in knowing I would with another being at the moment of my death if this car came off and plunged to the ground. (Yes, I was ABSOLUTELY having those kinds of thoughts!)
Our birthday person’s two friend in the front were doing well, though she wasn’t so keen on it…
One woman had her selfie-stick out and was snapping shots of all of us and the view. The other woman, sitting in the middle, was very easy going and relaxed. Clearly, these two weren’t experiencing anxiety like the rest of us.
“You have a very calming effect” my seat mate said.
“Doesn’t she?” my friend replied.
As we began our descent of the first rotation, my friend speculated “Maybe we only go around once…” with hope.
Coming down didn’t bother me at all, and my anxiety immediately receded as we finished our first rotation. When we didn’t stop, heading up again, my friend said “Well, then it’s only two rotations, because it’s not too busy.”
I was surprised by the return, in full force, of my pounding heart, fluttering stomach and general discomfort as we headed up for the second round. My seat mate was just as uncomfortable as she had been during our last trip up.
We did talk about our discomfort throughout the ride, and the other women were sympathetic to our reactions. It strikes me, in retrospect, that it must’ve helped that we didn’t have to contend with either teasing or well intentioned attempts to calm us with intellectual reasoning. There is nothing intellectual about this fear response.
Once we were on our descent for the second and thankfully final revolution, my anxiety dissipated and was gone by the time I embarked from the ride.
What has the Alexander Technique got to do with this story?
It is my long time study of the Alexander Technique that gave me the skill to summon my inner resources in the face of a frightening experience. I have learned how to stay more present in moments when I have historically panicked.
Part of my skill as a teacher of the Alexander Technique allows me to teach others to summon their inner resources, and the act of teaching gets my attention off my own internal reaction to things that trigger me. Taking care of my student, by teaching and modeling this self-soothing, is best taught by me actually self-soothing as I teach. It’s a win-win.
Alexander calls this self-soothing skill “inhibiting” – that is, interrupting a habitual cascade of responses to a trigger (Alexander referred to it as a stimulus), in order to stay more present to assess the current situation more accurately, in order to respond more appropriately to this moment, in this moment.
I have an old whiplash injury, so any abrupt impact, whether it’s front-to-back or side-to-side triggers my injury.
I skipped the kiddy rollercoaster, I don’t ride any rollercoasters, and I don’t do water rides.
I do fine with spinning rides, so bring on the Merry-Go-Round!
I know I can survive the Ferris Wheel, so if someone offers me a good enough incentive (I am seeing a $ with at least 3 zeros after it…) I can do it, but otherwise, there’s no reason for me to EVER ride one again…
[author] [author_image timthumb='on']http://www.acatnyc.org/main/wp-content/uploads/2014/01/Brooke1web.jpg[/author_image] [author_info]N. BROOKE LIEB, Director of Teacher Certification since 2008, received her certification from ACAT in 1989, joined the faculty in 1992. Brooke has presented to 100s of people at numerous conferences, has taught at C. W. Post College, St. Rose College, Kutztown University, Pace University, The Actors Institute, The National Theatre Conservatory at the Denver Center for the Performing Arts, Dennison University, and Wagner College; and has made presentations for the Hospital for Special Surgery, the Scoliosis Foundation, and the Arthritis Foundation; Mercy College and Touro College, Departments of Physical Therapy; and Northern Westchester Hospital. Brooke maintains a teaching practice in NYC, specializing in working with people dealing with pain, back injuries and scoliosis; and performing artists. www.brookelieb.com[/author_info] [/author]
Alexander Technique and Voice: An Interview With ACAT Teacher Training Student Ezra Bershatsky
 by Brooke Lieb
LIEB
by Brooke Lieb
LIEB
I began taking voice lessons with you, Ezra, recently, and have been fascinated with the process, and very grateful for your skill and clarity. We established that I haven’t injured my voice, since I don’t sing regularly and was lucky not to have any harmful teachers in the past. I think my ability to inhibit along with my blissful ignorance of “vocal technique” and my lack of attachment to what sounds I produce, has helped me explore what you are offering. I am excited to see how your practice evolves as a result of your progression through the TCP at ACAT. Tell me about how your lessons in the Alexander Technique have influenced your own singing?
BERSHATSKY
Well, I believe and teach that vocal technique is a state of being rather than something to do. I used to employ a vocal technique to sing rather than allow for a spontaneous, natural, mutable technique to evolve in response to music. Unsatisfied with my progress in the former, I eventually found functional voice training, which stresses spontaneity and function over aesthetic. The Alexander technique has helped me expand my awareness and curiosity for anything that might prevent my voice from organizing itself in response to vowel, pitch and intensity. I sing now with the added awareness of the floor I stand on, the space around me and the overall organization of my body, whereas before the Alexander technique the process of singing so fascinated me that all of my attention was focussed on singing and I was basically unaware of everything else, including where I was. This narrowing of focus isn't very conducive to spontaneity or freedom. The Alexander technique is my practical guide to explore the unexplored and helps me keep my bearings in unfamiliar lands.
LIEB
How has your work with Alexander Technique informed your work with your voice students?
BERSHATSKY
My first major realization was how important words are and how varied are students' responses to them. A lesson with an advanced student is almost completely devoid of spoken cues, relying on my piano playing and mouthing the vowel to be used for the exercise, while talking is mainly for validating an experience. But for new students, talking is very helpful. I was already used to customizing exercises for each student, but hadn't considered that wording could have such an effect on the outcome of an exercise. For instance, I used to tell students to "hold" a pitch, but discovered that this rarely happened without the student tightening somewhere in response of their desire to feel and grasp something. I now say “sustain" or merely indicate with a gesture from my hand instead. I used to use the word "attack" instead of "onset". I also now encourage my students to remain aware of their environment as they sing. I already strove to encourage a judgement-free environment where aesthetic is suspended and the student is permitted to experiment and release sound rather than manage it. The Alexander technique has given me more awareness of the impact of what I say and do and the responses they elicit in the student, so that I can communicate more effectively. When one approach fails I don't persist with it, but will rather look for another means that will facilitate a more organic, unhabitual response in the student. The most important benefit I am reaping is that I can teach for longer periods of time with less of a toll on my own body, use and vocal technique. When I first began to teach, much of my information about what the student was doing came from empathetically responding to the students’ use, so that when they sang poorly my throat would begin to ache or feel dry or I would notice what felt like my larynx trying to climb out of my throat. And after teaching a long day my body would complain and I'd be left feeling drained. The idea of "staying back and up" while I teach has been invaluable and helps me maintain awareness of what I'm doing as I listen to my students. The student benefits as much as I do as I hear more accurately and am less attached to any outcome. I still have the choice to allow my body to try on their misuse pattern but it's a choice now instead of a habit.
LIEB
Why did you decide to train as an Alexander Teacher?
BERSHATSKY
After a few Alexander teachers suggested I might enjoy training I started to seriously consider it. Especially after I began teaching voice to a graduate of ACAT, who pointed out some of the similarities between what I was teaching and The Alexander Technique. My primary draw to start training, however, was to improve my own use and understanding of the Technique.
LIEB
How do you see your work as a singer, voice teacher and Alexander Teacher evolving in the future?
BERSHATSKY
I'd like to have a private Alexander technique practice alongside my vocal studio. My plan is to use the next two years of my ACAT training to further hone my skills as a singer and teacher while learning repertoire along the way. When I finish training I want to do as many auditions as I can and get as much stage experience as possible. If I'm successful, my teaching practices will mostly be on hold, but the experience will add another dimension to my teaching and is crucial to my own happiness as a performer. I don't want to live vicariously through my students.
LIEB
What are some of the things you are working on as a teacher?
BERSHATSKY
I never want to limit my students with my aesthetic and this is an ongoing endeavour. To hear past aesthetic to the overall function. And to allow each student’s voice to be unique, as an expression of them, rather than of my idea of what their voice should be. I’m working on the clarity with which I communicate to each student. I'd love to get to the point where I consistently feel as good as the student does after a lesson. This is rarely the case at present, although the better I teach the better I feel during and afterwards.
LIEB
What do you love most about teaching voice, and teaching in general?
BERSHATSKY
I love watching as a student has a completely new experience. It's like watching a child taste ice cream for the first time. I imagine seeing the new neuronal pathways forming. I also love the trust that forms between teacher and student. I strongly believe that the burden of teaching should fall solely on me as the voice teacher and that there is no burden on the student to learn. Assuming the student who is willing to pay with their time and money is genuinely interested in improving, the student can't help but learn if they are being taught well.
[author] [author_image timthumb='on']http://www.acatnyc.org/main/wp-content/uploads/2014/01/Brooke1web.jpg[/author_image] [author_info]N. BROOKE LIEB, Director of Teacher Certification since 2008, received her certification from ACAT in 1989, joined the faculty in 1992. Brooke has presented to 100s of people at numerous conferences, has taught at C. W. Post College, St. Rose College, Kutztown University, Pace University, The Actors Institute, The National Theatre Conservatory at the Denver Center for the Performing Arts, Dennison University, and Wagner College; and has made presentations for the Hospital for Special Surgery, the Scoliosis Foundation, and the Arthritis Foundation; Mercy College and Touro College, Departments of Physical Therapy; and Northern Westchester Hospital. Brooke maintains a teaching practice in NYC, specializing in working with people dealing with pain, back injuries and scoliosis; and performing artists. www.brookelieb.com[/author_info] [/author]
Being A “Yes" to Life, Without Losing My Reason
 by Brooke Lieb
I have been involved in business and life coaching and spiritual communities that were all about being a yes. “Being a Yes” means looking on the positive side of things, going for it, not taking no for an answer, and with that, the dark underside of self recrimination, FOMO (fear of missing out), shame if I’m not being a yes, and the uncomfortable feeling that comes when you say yes in times when a “no” is more authentic.
by Brooke Lieb
I have been involved in business and life coaching and spiritual communities that were all about being a yes. “Being a Yes” means looking on the positive side of things, going for it, not taking no for an answer, and with that, the dark underside of self recrimination, FOMO (fear of missing out), shame if I’m not being a yes, and the uncomfortable feeling that comes when you say yes in times when a “no” is more authentic.
Over the years, I have come to recognize I have a number of patterns and cycles that are starting to feel out of balance. There have been long periods of time, years or more, when I have been in some form of business or life coaching, or trying different systems and strategies to create results in my personal or professional life, focusing on fitness, focusing on diet, shifting from one system to another. I have read hundreds of self-help books, and have been more or less systematic over the years at making steps to move towards having the life I think I want. I have been fortunate, with good health, access to education, employment and enough success to call my passion for the Alexander Technique my profession. I have experienced very few tragedies or economic challenges that caused me any prolonged stress. I don’t know how much of that is the result of my good fortune, good decisions, or my perception or interpretation of events and circumstances. I don’t know how much is because of how the Alexander Technique has given me access to my reason.
Even with all of that, my tendency is to avoid risk, keep my life simple and operate in a small orbit. I have many stories and rationalizations for why I don’t or can’t do certain things, and there are a lot of “no’s” in my moment to moment choices. I don’t mean saying no to a stimulus, I mean habitually saying “no”.
It ends up being an ongoing balancing act. Too many yes’s or too many no’s tend to throw me out of balance. Too many yes’s, and I can end up overcommitted, spread too thin, exhausted, coming up short, pushing too hard and irritable. Too many no’s, and I may start to feel lonely, isolated, and as though I am not taking advantage of what life has to offer.
How does the Alexander Technique help?
I have a process to assess where I am and what I am doing in the short and long term. If I consider "the need to choose" as a stimulus, the rest of Alexander’s process is consistent. Pause, inhibit my habitual response to “choosing”, send my directions, continue to send my directions while considering my choice in this more integrated state, and move forward. In the case of a decision, I may need to reevaluate and reassess as the choice plays out over time.
My choice may yield an unsuccessful outcome, but if I continue to work with Alexander’s process, I can make a new decision, change my strategy, and seek additional information to assist in how I respond to the outcome. There is always a new stimulus, there are always more moments of making decisions.
I am not implying that I, or anyone else, NEEDS the Alexander Technique in order to access what I have described here, and find balance in the moment. I don’t know, however, how it happens without the Alexander Technique in the mix, because for me, the Alexander principles have been part of the equation for my “balancing act" since I was 20. Considering my peers and family members who haven’t had Alexander principles at their disposal, I would bet good money that I can give credit (lots of it!) to Alexander Technique for helping shape my life, and giving me a way to continue to find that delicate balance.
If you are intrigued by this idea, be sure to visit www.acatnyc.org to find out how you can start learning Alexander principles to help you find more balance in life.
[author] [author_image timthumb='on']http://www.acatnyc.org/main/wp-content/uploads/2014/01/Brooke1web.jpg[/author_image] [author_info]N. BROOKE LIEB, Director of Teacher Certification since 2008, received her certification from ACAT in 1989, joined the faculty in 1992. Brooke has presented to 100s of people at numerous conferences, has taught at C. W. Post College, St. Rose College, Kutztown University, Pace University, The Actors Institute, The National Theatre Conservatory at the Denver Center for the Performing Arts, Dennison University, and Wagner College; and has made presentations for the Hospital for Special Surgery, the Scoliosis Foundation, and the Arthritis Foundation; Mercy College and Touro College, Departments of Physical Therapy; and Northern Westchester Hospital. Brooke maintains a teaching practice in NYC, specializing in working with people dealing with pain, back injuries and scoliosis; and performing artists. www.brookelieb.com[/author_info] [/author]
Seven Questions with ACAT Teacher Training Student Tim Tucker
 by Brooke Lieb
Q. What, if anything, did you learn from putting hands on faculty?
by Brooke Lieb
Q. What, if anything, did you learn from putting hands on faculty?
A. ACAT's faculty offers me the ultimate laboratory to test my skills as a budding Alexander Technique teacher. The faculty is incredibly sensitive to the messages I'm transmitting, or not transmitting, through my hands and can quickly diagnose and tactfully communicate what my hands are up to. The learning that putting hands on faculty permits is quite unlike what happens when working with fellow trainees or supervisory students -- faculty feedback and guidance has repeatedly taken my practice of the AT to a whole new level.
Because I tend to "try too hard" and am often "highly serious" my work with faculty also helps to address those particular habits in the context of my attempts to teach them. I'm repeatedly offered the chance to lighten up and do less when working with my hands on the teachers, and to see how easing up can make me a better teacher and my teaching practice more sustainable.
Q. Did you observe direction in your teacher when you put hands on her or him?
Teachers at ACAT offered me vivid direction -- sometimes consciously amplified by them because of where I was in the training process -- whenever I put hands on them.
Q. If you did observe direction in your teacher, did the experience illuminate the concepts of AT, the actual mechanism of h/n/b integration/primary control, or any of F. M.'s ideas from his writings?
Teachers know when I'm inhibiting, and when I'm not. And they illustrate, sometimes overtly and sometimes implicitly, the impact of inhibition coming through my hands on their nervous systems and coordination.
Q. How did the supervised teaching in the third year contribute to your learning, and/or prepare you for teaching on your own?
Having faculty observe and participate in supervised teaching has been a boon for me as a trainee. Often supervisory students exhibit patterns of misuse that I have not encountered before on the training course; having faculty immediately available to answer my questions and offer suggestions regarding a student's misuse takes the pressure off in challenging teaching situations and supports my learning. Meanwhile, faculty often put hands on me as I put hands on my student, helping me to come back to my own use and address my own habits as the foundation from which my teaching must originate. Lastly, the opportunity to discuss each supervisory session with faculty and colleagues after the students leave has helped me to gain more insight from my own experience and to learn from my colleagues as well.
[author] [author_image timthumb='on']http://www.acatnyc.org/main/wp-content/uploads/2014/01/Brooke1web.jpg[/author_image] [author_info]N. BROOKE LIEB, Director of Teacher Certification since 2008, received her certification from ACAT in 1989, joined the faculty in 1992. Brooke has presented to 100s of people at numerous conferences, has taught at C. W. Post College, St. Rose College, Kutztown University, Pace University, The Actors Institute, The National Theatre Conservatory at the Denver Center for the Performing Arts, Dennison University, and Wagner College; and has made presentations for the Hospital for Special Surgery, the Scoliosis Foundation, and the Arthritis Foundation; Mercy College and Touro College, Departments of Physical Therapy; and Northern Westchester Hospital. Brooke maintains a teaching practice in NYC, specializing in working with people dealing with pain, back injuries and scoliosis; and performing artists. www.brookelieb.com[/author_info] [/author]
Thoughts on Doing and Non-Doing
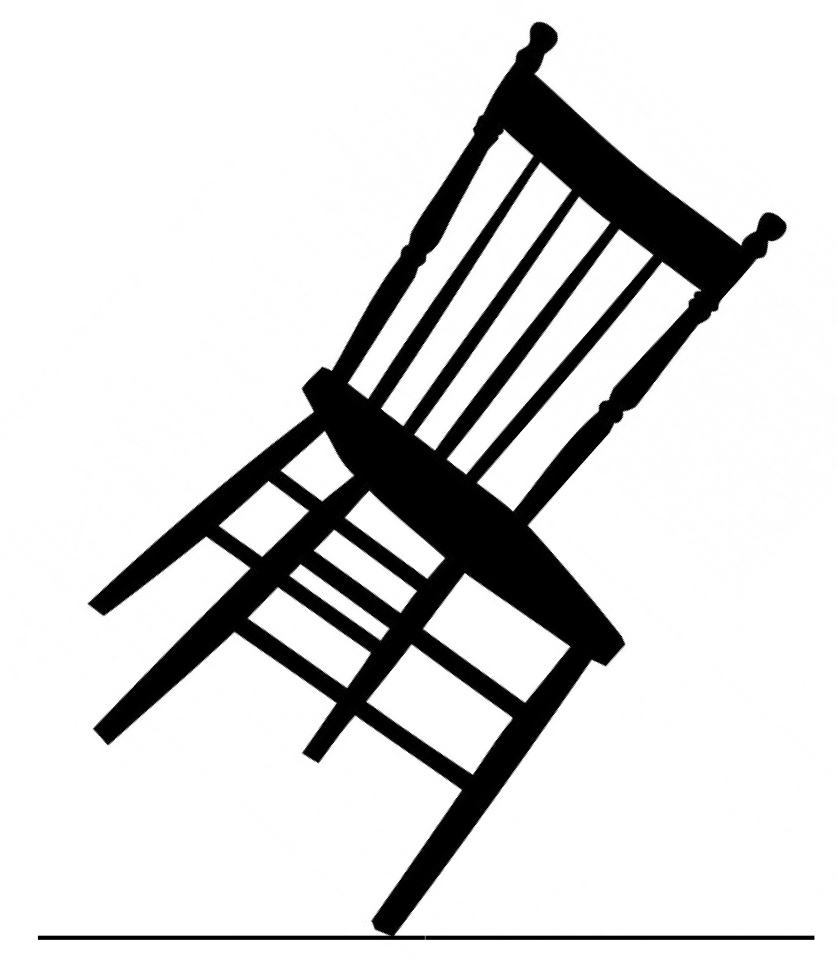 by Ezra Bershatsky
It is almost irresistible to become fascinated with the philosophies that are so perfectly compatible with the Alexander Technique; to revel in the Zen-like mysticism it inspires: “The chair lifts; I don’t lift it," or "I am breathed." For some, this is confirmation of what they already believe. However, I think this only serves to obscure for others and even ourselves what is actually happening.
by Ezra Bershatsky
It is almost irresistible to become fascinated with the philosophies that are so perfectly compatible with the Alexander Technique; to revel in the Zen-like mysticism it inspires: “The chair lifts; I don’t lift it," or "I am breathed." For some, this is confirmation of what they already believe. However, I think this only serves to obscure for others and even ourselves what is actually happening.
This topic is of especial interest to me as I have found a wealth of knowledge in the Tao Te Ching: “Wei wu wei,” or “doing without doing,” is a prevalent theme throughout the text, and it offers considerable insight into various implications of The Alexander Technique. As pointed out by Walter Carrington, we cannot lead a life of non-doing, as we would inevitably starve to death. Carrington says that muscular activity in the body is obviously doing; however, to me this is anything but obvious. Would anyone say, “I’m doing my heartbeat?” Another way to define “doing” is as any volitional or potentially volitional muscular response. I say potentially, as the vast majority of muscular responses and coordinations are allocated unconsciously by the brain through the stimulus of a desired outcome.
Doing without doing is a way of accomplishing an end while avoiding an habitual means to obtain it. This might be achieved by changing one's immediate intention, thus delaying the ultimate outcome. For instance, if my goal is to sit in a chair, I can decide merely to sit, which would trigger a complex muscular coordination involving hundreds of muscles contracting and releasing simultaneously and sequentially. My desire to quickly carry out the action of sitting might allow for little new input into achieving the action, so that if the chair is lower than the average chair, I will probably fall into it, expecting to have been sitting sooner. If I wanted to employ a "non-doing" approach, I could first try to have my desire to sit become the outcome of another intention: my knees bending. If I continuously bend my knees, eventually I will make contact with the chair. Such an exercise would begin to reeducate me from my habitual way of sitting, so that when next I go to sit in a "doing" or habitual manner, it might happen more efficiently. It should be said that this improvement will most likely revert quickly to my more habitual behavior shortly thereafter, unless this type of work continues.
It is our goal to accomplish any end by finding a way to allow a spontaneous coordination instead of imposing one; to consider how this action will be achieved instead of predetermining it; to avoid habitual response patterns and allow for spontaneous ones, even if the latter are at first clumsy or less efficient. Once we have established clarity about this goal, the implications for similar or seemingly related philosophies and mystical ideas can be safely considered, and will not be conflated with the principles and workings of the Alexander Technique.
[author] [author_image timthumb='on']http://www.acatnyc.org/main/wp-content/uploads/2016/07/Ezra-Bershatsky-by-Sandro-Lamberti-Photography-23.jpg[/author_image] [author_info]EZRA BERSHATSKY—A graduate of The Juilliard School Pre-College Division, Ezra has two Bachelor degrees of Music from Mannes College The New School for Music, in vocal performance and musical composition. He is currently training to be a teacher of the Alexander Technique. He has been singing and performing since childhood, and early in his training he discovered that he has a passion not only for making music, but for teaching others. Ezra teaches voice in New York City on the upper west side. [/author_info] [/author]
Taking Action: How Does That Work in the Context of the Alexander Technique?
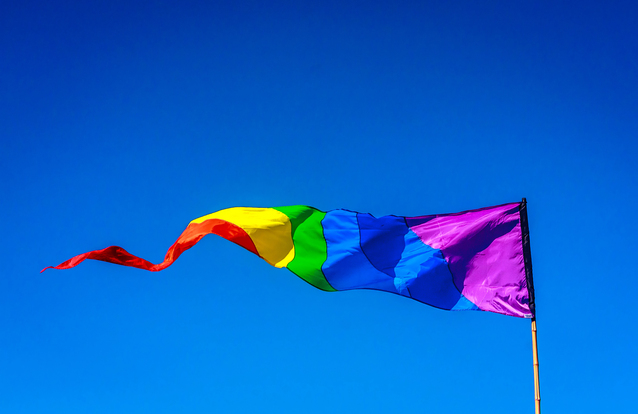 by Brooke Lieb
by Brooke Lieb
In light of the recent hate crime, the mass killing in Orlando targeting the LGBTQ community on June 12, I thought about what it was to respond with meaningful, integrated action.
What has this got to do with the Alexander Technique? Alexander Technique often emphasizes “non-doing” which can be mistaken for inaction. Non-doing is more about having the time and space to unpack a response to find what may be habitual and automatic, and gain access to a conscious, reasoned response.
Working with this paradigm gives me a way to question the accuracy or validity of my feelings, both those I label as sensations, and those I label as emotions. I can also question the habits I have around using those feelings to guide my behavior and actions. I don’t want to respond to this latest tragedy comfortably or in my familiar and habitual way, I want to respond accurately and in measure with my examined belief systems.
I want to communicate with the people who feel particularly at risk of being targeted because of who they love or how they look, a danger that may be even more in the forefront of their day to day lives, as a result of this recent atrocity. I want to offer my support. But for me, my kind words are empty if my actions and behavior don't have the potential to generate a safer world for them.
I want to show empathy and connect with my friends and loved ones to show that I care about this issue and it breaks my heart that people are being murdered because of some distorted set of artificial values held by others. Those beliefs are what make some of us a threat to others of us.
I saw a number of posts about taking action, as the more impactful response to this latest in a “much too frequent and much too long” string of mass killings.
So I went to google to find out how to take action. I donated to the Brady Campaign, I signed a petition which I was informed was equivalent to writing a letter.
I wrote to both of my state senators to say I am a constituent who supports strict gun control, and when considering the second amendment as written: "A well-regulated militia being necessary to the security of a free state, the right of the people to keep and bear arms shall not be infringed” I support limiting access to and the use of guns to the confines of a well-regulated militia.
So, yes, I have been crying since Sunday, June 12, and looking at my transparent biases and bigotry to take responsibility for the ways I may have inadvertently contributed to the climate in our country by being ignorant and unable to see what I may be a party to. I see that my inaction contributes to the status quo. By the way, I was raised around activists, growing up in the late 60’s and early 70’s, and I take a lot for granted because so many took action during that time in history.
What has this got to do with the Alexander Technique? I am saying “no" to my comfortable habit to remain silent while feeling hopeless. I often keep silent out of my desire to appear non-judgemental and neutral so my clients won’t feel judged in my hands. Silence can be useful in some situations, but silence can also be a way to stay comfortable and ineffective.
So, instead, I am taking action, and being non-habitual by using my literal and literary voice to express my fondest wishes and hopes - that we take the actions needed so we live in a world that values all human life and celebrates creativity and diversity in how we each express ourselves. I wish to live in a world where no one is in danger from another, because of what they have or don’t have, for what they believe or don’t believe. And that we don’t use our personal beliefs to injure each other.
If you want to learn more about some possible actions to take, here are some links:
Contact your congressional representative: http://www.house.gov/representatives/find/
Contact your Senator: http://www.senate.gov/senators/contact/
How did your senator vote on background checks?: http://everytown.org/senate-votes/?source=etno_ETActPage&utm_source=et_n_&utm_medium=_o&utm_campaign=ETActPage
Tweet your congressperson: http://everytown.org/tweet-at-congress/?source=etno_ETActPage&utm_source=et_n_&utm_medium=_o&utm_campaign=ETActPage
Support the Brady Campaign to end gun violence: https://secure.bradycampaign.org/page/contribute/center-enough
[author] [author_image timthumb='on']http://www.acatnyc.org/main/wp-content/uploads/2014/01/Brooke1web.jpg[/author_image] [author_info]N. BROOKE LIEB, Director of Teacher Certification since 2008, received her certification from ACAT in 1989, joined the faculty in 1992. Brooke has presented to 100s of people at numerous conferences, has taught at C. W. Post College, St. Rose College, Kutztown University, Pace University, The Actors Institute, The National Theatre Conservatory at the Denver Center for the Performing Arts, Dennison University, and Wagner College; and has made presentations for the Hospital for Special Surgery, the Scoliosis Foundation, and the Arthritis Foundation; Mercy College and Touro College, Departments of Physical Therapy; and Northern Westchester Hospital. Brooke maintains a teaching practice in NYC, specializing in working with people dealing with pain, back injuries and scoliosis; and performing artists. www.brookelieb.com[/author_info] [/author]
Returning Home
 by Mariel Berger
Many thanks to my Alexander Technique teachers: Witold Fitz-Simon and Jane Dorlester.
by Mariel Berger
Many thanks to my Alexander Technique teachers: Witold Fitz-Simon and Jane Dorlester.
For a lot of people, sexual intimacy is an attempt to return to our bodies and feel whole. We spend so much time in our heads, experiencing life not fully in our bodies, not feeling the integration of our system. There is so much fixation on finding a partner and experiencing intimacy as a way to feel connected and validated. Through Alexander Technique we practice feeling whole so that we don’t need to be in our front bodies grasping for more. We can be aware of our back bodies, our head moving forward and up, neck free, torso widening and deepening, knees moving forward and away. All of the parts create a simultaneous awareness of the whole: one at a time and all together.
A lot of the pain I experience in life comes from a feeling of being disconnected and isolated. There’s a quote I love by Lawrence LeShan, “It is the splits within the self that make for the feeling of being cut off from the rest of existence.” I am slowly learning how to experience myself without all the splits -- to gather all my different sides --shawdowed and bright -- and hold them into a unified whole.
This past winter I was severely depressed and felt as if my Self were fragmented into tiny meaningless pieces. I felt alone in my head, and disconnected from myself, loved ones, or any purposeful connection. My mind was full of vicious and self-loathing thoughts, and I tried to escape the abuse by fleeing from my body and myself and towards someone I was romantically interested in. I have learned, again and again though, that true resolution comes from staying -- creating space for the pain, witnessing it, holding it, and integrating it into my whole self. If I try to reach outside of myself to escape pain, that only takes me further from home.
I recently took a course on Visceral Manipulation, taught by Liz Gaggini. We learned that in order to heal a client’s organ, you must have an attitude of nonchalance and only put some of your attention on the person. The rest of your attention will stay in your body, in the room around you, and beyond. In order to heal another, you must stay whole. If you give too much, you offer the person a fragmented presence, an energy that is coming just from the front of the body -- a grasping, an end-gaining.
This is so true for relationships. When connecting with another person, even someone to whom I’m greatly attracted, I can practice not coming forward into the pull of hormones and craving, but remain in my full body. There is much pleasure to feel just here as I am, inside myself. This is a new and exciting practice, to realize that simply walking around and being inside my body can feel good, especially after the last 5 years of chronic pain and health problems. I am learning how to hold pain as part of the experience, not the only thing. I am learning to accept all the parts of myself, and to hold them in an awareness that is deep and fulfilling.
This past winter I liked someone so much that I lost my awareness of my back body. I fell forward. I fell hard.
And the ironic thing is, I was leaning forward in order to feel a connection -- to return home. But home is back and up into my torso, widening and deepening, my head moving forward and up, my gaze softening, my neck being free.
Here I am again, having remembered, but life is a process of forgetting and remembering, of getting lost in the pieces, and then expanding our awareness to perceive more. Alexander Technique is the gentle practice each day to return to our whole.
[author] [author_image timthumb='on']http://www.acatnyc.org/main/wp-content/uploads/2015/07/helsinki-sun-headshot.jpg[/author_image] [author_info]MARIEL BERGER is a composer, pianist, singer, teacher, writer, and activist living in Brooklyn, NY. She currently writes for Tom Tom Magazine which features women drummers, and her personal essays have been featured on the Body Is Not An Apology website. Mariel curates a monthly concert series promoting women, queer, trans, and gender-non-conforming musicians and artists. She gets her biggest inspiration from her young music students who teach her how to be gentle, patient, joyful, and curious. You can hear her music and read her writing at: marielberger.com[/author_info] [/author]
Epiphany
Cate9thTerm-Judy
by Cate McNider
As a soon-to-graduate Alexander Technique teacher, my time at ACAT, and why I embarked on this Alexander journey, has crystallized into this realization: I love epiphanies and live for them! I love that moment when ‘I get it’. That is in the direction of the UP for me. That realization is the inner up that supports the physical going up. Getting out of my own way, and allowing my head to go forward and up is what allows the space to receive information from my consciousness. We focus a lot on the physical habits and procedures to enliven our dynamic oppositions in this biomechanical suit we call a body, and it works. What underlies the physical is our curiosity, our innate impulse to rise, to evolve, to discover who we are, to be ourselves. That journey is a process, the process is a journey. It is the best investment we can ever make, to take that journey consciously, to think in activity, to be aware of what we are doing to and with ourselves, and how those habits are reflected back to us in the world.
It is this love of deepening understanding that makes me curious about how can I help this person, this student, realize they are compressing themselves and that they can stop whatever the habit is and dis-cover the un-ease and allow the ease to reveal itself.
Words are always a problem. For example, how I mean these words and how I am crafting them to communicate a feeling to you may not be what you hear or understand, which is where the hands come in to give you an experience of the AT principles and how that applies to you personally. Most of us share some variation of the ‘back and down’, but how that manifests in our neural network is unique and individual. Many books are written about the AT and the authors themselves struggled to various degrees to describe what FM was doing and what the principles point towards.
The quality of the touch is what takes three years to ‘get’, to just begin this ‘teaching’ journey, to allow the energy of the thought to be transmitted to the student’s whole wedded self. The epiphanies come more often after 3 years of study because I am pausing enough, thus more available for what comes through me and to me, the result of ‘getting out of the way’.
And this communal moment of ‘inhibition’ when the teachers hands are on me, and we are thinking together, powerful change occurs. This ability to change is within all of us. If we don’t let go of the old that no longer serves us, we wear it on our body, as the wind shapes the sand, and our lives repeat old outcomes. Breaking out of a cycle of any psychophysical habit is enhanced by practicing the principles and like a run in stockings, it runs both ways.
How you read this is how YOU read this. What I wrote is what I have real-ized. Take your own trip and find out for yourself!
[author] [author_image timthumb='on']http://www.acatnyc.org/main/wp-content/uploads/2015/12/McNider.jpeg[/author_image] [author_info]CATE MCNIDER is in her final term at ACAT and soon to graduate (all requirements being completed)! She has been a bodyworker since 1991, also practitioner certifications in Body-Mind Centering® and Deep Memory Process®. She is a dancer, poet and painter (see youtube). She most recently performed a piece called: ‘Habit and Non-doing‘ at Dixon Place. Her art can be seen at: www.artsicle.com/Cate-McNider and contacted thru her website: www.thelisteningbody.com. Many thanks to all my teachers, volunteer teachers and fellow trainees at ACAT.[/author_info] [/author]
Five Questions with ACAT Teacher Training Program Alumna Barbara Curialle
 by Brooke Lieb
Barbara Curialle graduated from the ACAT Teacher Training Program in June 2009.
by Brooke Lieb
Barbara Curialle graduated from the ACAT Teacher Training Program in June 2009.
Q. What made you decide to train as an Alexander Technique teacher?
A. Many years ago, I saw a former piano student of my teacher play the same piano piece before and after 2 years of Alexander lessons. He was completely transformed, and his playing—stiff and constrained the first time—had become open and joyous. It was many more years before I was able to take lessons, but my first teacher—Nina D’Abbracci—encouraged me to do the training.
Q. Why did you choose ACAT's training program?
A. I chose ACAT because it was the first program in the U.S. and because of the faculty’s amazing credentials and backgrounds.
Q. What, if anything, did you learn from putting hands on faculty?
Once I got over my initial nervousness, I appreciated the guidance—especially the verbal portion—from the faculty. Everyone’s friendly encouragement and appreciation of my efforts was a tremendous boost to my confidence. I also appreciated the opportunities to work with many faculty members: Everyone’s use and comments were different, but they all helped me integrate my own thinking.
Q. Did you observe direction in your teacher when you put hands on her or him?
A. Yes! I think that at first I was expecting some dramatic, large-scale change, but the changes I noticed were more subtle than that.
Q. If you did observe direction in your teacher, did the experience illuminate the concepts of AT, the actual mechanism of h/n/b integration/primary control, or any of F. M.'s ideas from his writings?
A. Yes, the experience did illustrate the AT concepts and especially HBN integration/primary control. In terms of F. M.’s ideas and writings, the connection was more subtle but still strong.
Q. How did the supervised teaching in the third year contribute to your learning, and/or prepare you for teaching on your own?
A. I’m glad I had the experience of teaching with supervision. Having a faculty member there when I ran into a problem was very helpful. Again, having so many different viewpoints that all led to the same goal enriched and validated my learning experience immeasurably and helped me to formulate my own goals for working with students and making the work my own.
[author] [author_image timthumb='on']http://www.acatnyc.org/main/wp-content/uploads/2014/01/Brooke1web.jpg[/author_image] [author_info]N. BROOKE LIEB, Director of Teacher Certification since 2008, received her certification from ACAT in 1989, joined the faculty in 1992. Brooke has presented to 100s of people at numerous conferences, has taught at C. W. Post College, St. Rose College, Kutztown University, Pace University, The Actors Institute, The National Theatre Conservatory at the Denver Center for the Performing Arts, Dennison University, and Wagner College; and has made presentations for the Hospital for Special Surgery, the Scoliosis Foundation, and the Arthritis Foundation; Mercy College and Touro College, Departments of Physical Therapy; and Northern Westchester Hospital. Brooke maintains a teaching practice in NYC, specializing in working with people dealing with pain, back injuries and scoliosis; and performing artists. www.brookelieb.com[/author_info] [/author]
ACAT's Alexander Technique Teacher Certification Program: Supervised Teaching Component
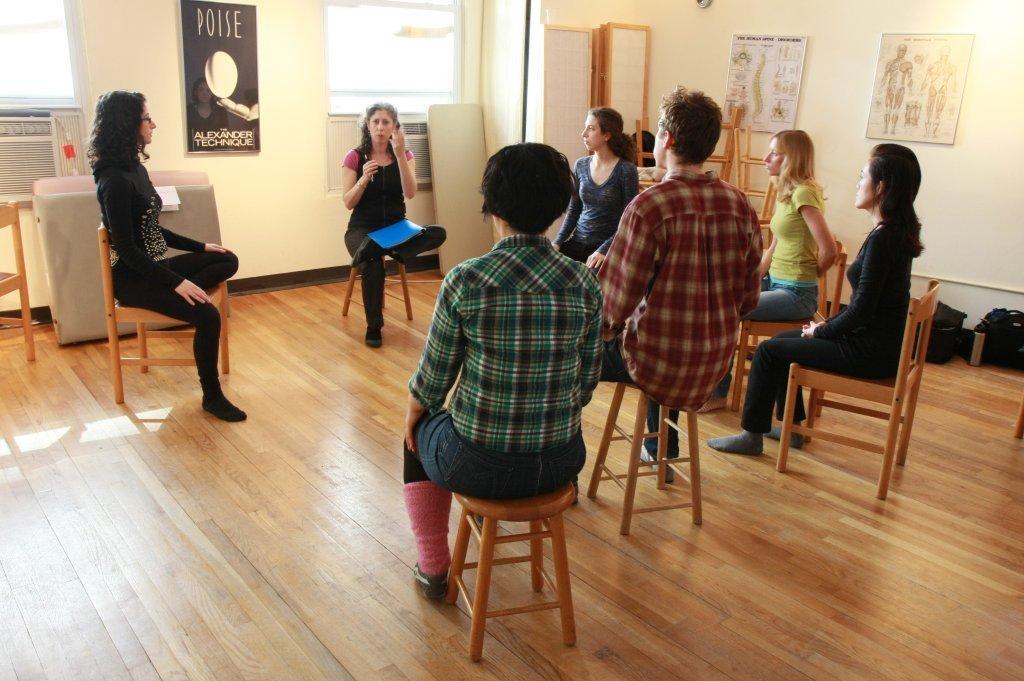 by Brooke Lieb, ACAT Training Director
ACAT’s Teacher Certification Program follows a developmental curriculum, which has been refined over the last 49 years. Our program is designed so that our graduates are prepared, and more importantly, are confident about their ability to teach, by the time they receive their teaching certification.
by Brooke Lieb, ACAT Training Director
ACAT’s Teacher Certification Program follows a developmental curriculum, which has been refined over the last 49 years. Our program is designed so that our graduates are prepared, and more importantly, are confident about their ability to teach, by the time they receive their teaching certification.
Throughout the course, students are being taught hands on skills, sometimes being guided through activities with the assistance of the teacher, and sometimes putting hands on the faculty to receive specific and customized instruction. At the core of effective hands on skills is always our own application of the principles to ourselves. Students come to understand and develop proficiency in applying Alexander Technique principles to all their activities, including the hands on and verbal components of teaching. How we are each applying those skills is at the heart of everything that we do in life, including providing instruction to another. Graduates have typically taught a minimum of 58 sessions under supervision by the time they graduate. I trained at ACAT from 1987 to 1989, and I, too, felt fully prepared and confident about my abilities to work with students by the time I completed my training.
Here's what Karen Krueger, who graduated in December 2010 and who has served on ACAT's board of directors, had to say about the experience:
"Supervised teaching in the third year was a vital bridge from working with my trainers and fellow trainees to teaching on my own.
"Like ACAT's entire curriculum, the supervised teaching class follows a clear sequential structure. Although it was always challenging, it never seemed impossible. Week by week, throughout the year, my skills grew gradually, until I was able to teach an entire lesson to a beginning student. This was perfect training for becoming a teacher in private practice, since at the beginning, most of my students were also beginners.
"In the first term of our third year, our supervisory students had significant previous experience with the Alexander Technique. We then moved on to less experienced students, and we worked with beginners in our last term. As the experience level of our students decreased, the expectations of us as teachers-in-training increased: starting with 10- or 15-minute segments of teaching specific elements of the technique, and building up to teaching 45-minute lessons. Throughout the process, our trainers were in the room with us, helping as needed. At the end of each teaching session, we had the opportunity to discuss what had happened with our classmates and the supervising teacher.
"Throughout the year, I got to try out different approaches to teaching, and to experience many real-world challenges, in a safe and supportive environment, in which both my students and my trainers were there to contribute to my learning. I also took advantage of the opportunity to teach a few private students outside class during my 9th term, and this, too, played an important role in my development as a teacher.
"The Alexander Technique teaches us to set aside undue focus on a goal, and to give attention instead to the "means whereby" -- the way in which we go about the activities involved in reaching the goal. This approach to learning is exemplified in the third-year supervised teaching curriculum at ACAT. And it works: when I graduated from ACAT, I felt fully confident in my ability to teach from day one."
[author] [author_image timthumb='on']http://www.acatnyc.org/main/wp-content/uploads/2014/01/Brooke1web.jpg[/author_image] [author_info]N. BROOKE LIEB, Director of Teacher Certification since 2008, received her certification from ACAT in 1989, joined the faculty in 1992. Brooke has presented to 100s of people at numerous conferences, has taught at C. W. Post College, St. Rose College, Kutztown University, Pace University, The Actors Institute, The National Theatre Conservatory at the Denver Center for the Performing Arts, Dennison University, and Wagner College; and has made presentations for the Hospital for Special Surgery, the Scoliosis Foundation, and the Arthritis Foundation; Mercy College and Touro College, Departments of Physical Therapy; and Northern Westchester Hospital. Brooke maintains a teaching practice in NYC, specializing in working with people dealing with pain, back injuries and scoliosis; and performing artists. www.brookelieb.com[/author_info] [/author]
Nine Questions with Alexander Technique Teacher Bob Britton
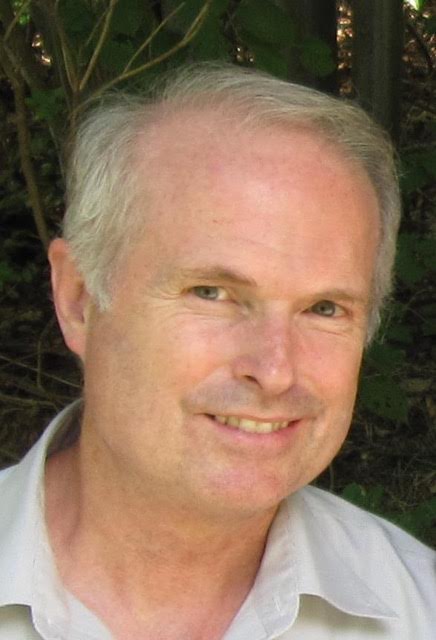 by Anastasia Pridlides
by Anastasia Pridlides
We are so pleased to have visiting teacher Bob Britton presenting a workshop—"Tuning Direction"—and there is still space for you to join us at ACAT on Saturday May 14th at 1pm. In advance of him joining us in our space we thought we would ask him a few questions to introduce him to the community.
Q. How long have you been teaching?
A. I first started taking lessons in 1974, and graduated as an Alexander Technique teacher in 1978.
Q. What was your first exposure to the Alexander Technique?
A. I first experienced the Alexander Technique because I had a knee injury as a result of sitting intensively in Zen meditation. A friend recommended that I try taking a lesson with Frank Ottiwell after I found out that the surgery for my knee injury would be a major operation. As soon as I walked into the lesson Frank noticed that my habitual style of walking was awkward because I habitually carried my right foot pointing out to the side ever since I had broken my leg when I was 10 years old. Frank asked me to completely relax my leg and then to drop the foot to the floor. My foot came down pointing straight ahead. Frank then asked me to take a step and I put it down with the toe facing out to the side. Frank said, “You see the foot knows where it wants to go, but you think the foot should be pointing out to the side.” I was amazed that what I was doing with my foot would make a difference in my knee. Gradually after six weeks of lessons my foot gradually came back around to pointing ahead as Frank introduced me to the larger organization of my whole body. Then the knee problem basically took care of itself and healed. I was impressed!
Q. What made you decide to become a teacher of this work?
I was not planning on becoming an Alexander teacher while I trained. I really was training to deepen my own experience of this marvelous work. After I graduated many people started coming up to me with ailments and the Technique was quite successful in helping them out. So when I left the Zen community it was a very natural choice to pursue the way of life of being an Alexander teacher.
Q. What most excites you about your upcoming workshop at ACAT?
A. Teaching workshops in the Alexander Technique is always energizing and gratifying. Somehow, thanks to human evolution, when we are sharing knowledge and skills about moving with more grace and efficiency everyone has a chance to experience joy and satisfaction. This is because our nervous systems are not neutral about the experience of moving with more efficiency. If we are moving with more skill we have more of a chance of survival, and the nervous system rewards us with endorphins. Of course working with old friends and new teachers who want to learn is always is a delight.
Q. What is your favorite way to engage with the AT in your daily life right now?
A. My favorite way of engaging with the Technique is organizing myself dynamically upward each morning, and throughout the day, especially by allowing my ribs to move buoyantly upward and engaging with the engaging with the environment around me. Meeting life from a dynamic and energetic organization is a true pleasure.
Q. What is most fascinating to you about the AT today?
A. Our human vertebrate structure is very, very old, and tuning into its beauty and brilliance is constantly refreshing. In addition, I love refining and finding more depth and sophistication in Alexander’s work.
Q. What is the most surprising effect your study of the AT has had on your life?
A. My experience is that everything changes with our posture. When our posture is dynamic, expanded, and engaged with our environment, the freshness of being happens. This is possible in every moment. The Alexander Technique is the best thing we can do in the present moment to improve our quality of being.
Q. Tell us about an interest/skill/passion of yours other than of the Alexander Technique.
A. One passion I am following now is going out with my local astronomy club to observe our Universe from dark sky locations. To be peering through my telescope and suddenly see the light from a distant galaxy that left there millions of years ago and now is arriving inside of my eye, is a rather awesome experience.
About Bob
Robert Britton graduated in 1978 from the Alexander Training Institute-SF (Frank Ottiwell and Giora Pinkas). In addition to his private practice in San Francisco, he has taught the Alexander Technique to musicians at the San Francisco Conservatory of Music since 1984. He served as the Chairman of the American Society for the Alexander Technique, and was a director of the 2011 International Congress of the Alexander Technique. He has helped train Alexander Technique Teachers since 1989, and regularly gives workshops to Alexander Teachers around the World.Find out more about Bob at uprighthuman.com
There are still a few spaces left in Bob's workshop. Go here to find out more and to register.
[author] [author_image timthumb='on']http://www.acatnyc.org/main/wp-content/uploads/2014/05/Anastasia.jpg[/author_image] [author_info]ANASTASIA PRIDLIDES teaches Alexander Technique, Bellydance and Yoga in New York City. Studying the Alexander Technique has been a deeply transformative and life changing process for her. Every day she wakes up excited to know that her job is share it with others. You can find her at movementhealingarts.com[/author_info] [/author]








